he group of nutrients known as omega-3 fatty acids is necessary for maintaining you health. They are polyunsaturated fatty acids that have numerous advantages for a person’s health. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) are the three main forms of omega-3 fatty acids.
While ALA comes predominantly from plant-based sources, EPA and DHA are primarily found in fatty fish. These fatty acids are regarded as necessary since the human body is unable to manufacture enough of them, necessitating dietary sources for their supply.
Because of the possible benefits they may have on a number of health-related factors, omega-3 fatty acids have attracted a lot of interest. Their impact on heart health, cognitive function, reducing inflammation, joint health, eye health, and mood management has received substantial research. Omega-3 fatty acids may boost cognitive growth and mental health, lower the risk of cardiovascular illnesses, reduce inflammation and joint discomfort, and improve general well-being, according to research.
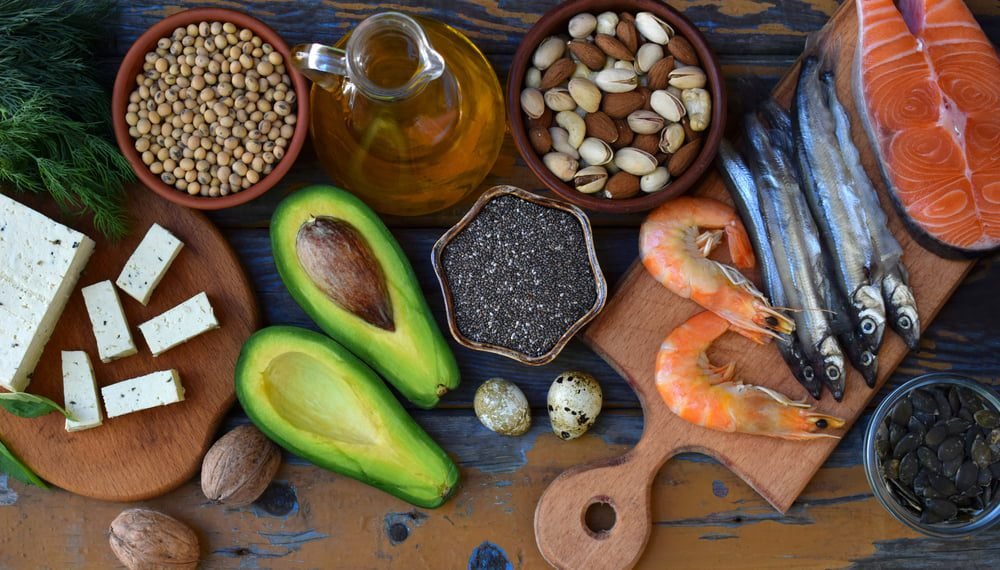
While fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are great wellsprings of EPA and DHA, plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and pecans give ALA. Notwithstanding, it’s critical to take note of that the change of ALA to EPA and DHA in the body is restricted. Accordingly, for people who don’t consume enough fish or have explicit dietary limitations, omega-3 enhancements, for example, fish oil or green growth based supplements, might be thought of.
Omega-3 fatty acids are fundamental supplements that offer an assortment of medical advantages. Enhancing them or remembering them for an even eating routine when fitting can work on generally speaking wellbeing and prosperity. In any case, it is consistently fundamental to counsel a clinical expert for exhortation that is explicitly custom-made to your necessities and conditions.
What is Omega 3 Fatty Acid
The polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) known as omega-3 fatty acids are vital for human health and play significant roles in a number of physiological processes. The following three categories of omega-3 fatty acids:
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): EEPA is basically tracked down in greasy fish, like salmon, mackerel, horse mackerel, and sardines. It is known for its mitigating properties and is gainful for heart wellbeing.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): DHA is additionally tracked down in greasy fish, as well as in green growth and particular kinds of microorganisms. It is a significant part of the cerebrum and assumes a pivotal part in mental health and capability. DHA is additionally significant for eye wellbeing.
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): ALA is the plant-based omega-3 unsaturated fat and is found in different plant sources, including flaxseeds, chia seeds, pecans, and soybeans. ALA can be changed over into EPA and DHA in the body, albeit the transformation isn’t extremely effective. Regardless, ALA actually offers some medical advantages.
Omega-3 fatty fats are frequently prescribed for their capability to reduce aggravation, support heart well-being, work on mental health, and Advantage in overall prosperity.
Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids offer several health benefits due to their important roles in various physiological processes. Here are some potential health benefits associated with omega-3 fatty acids:
- Heart Health: Omega-3 fatty fats, especially EPA and DHA, have been displayed to make cardioprotective impacts. They can assist with reduce fatty oil levels, lower circulatory strain, forestall the development of blood clots, and lessen aggravation in the supply routes. These advantages add to a decreased risk of cardiovascular sicknesses, like coronary illness and stroke.
- Brain Health and Cognitive Function: DHA, a significant part of the brain, is critical for mental health and capability. Omega-3 fatty acids are accepted to help mental capability, memory, and by and large cerebrum well-being. Sufficient admission of omega-3s has been related with a lower hazard of mental degradation and may help in lessening the gamble of neurodegenerative diseases, like Alzheimer’s disease.
- Inflammation and Joint Health: Since omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory effects, they can assist the body lessen chronic inflammation. They may lessen joint pain and stiffness and offer relief from inflammatory disorders like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Eye Health: Within the eyes, DHA serves as a fundamental building block of the retina’s structure. Adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, is important for maintaining good vision and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and dry eye syndrome.
- Mood and Mental Health: Omega 3 fatty acids might emphatically affect temperament and mental health. Their ability to lessen the signs and symptoms of bipolar illness, anxiety, and sadness has been researched. According to research, taking supplements high in omega-3 fatty acids may aid with mood and emotional health.
- Pregnancy and Early Development: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, are essential during pregnancy and early childhood for proper brain development and vision in the fetus and infant. sufficient intake of omega-3s during pregnancy has been associated with improved cognitive function in children.
It’s essential to note that while omega-3 fatty acids offer potential health benefits, individual results may vary, and it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance. Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids should be consumed as feature of a balanced diet and not as a substitute for medical treatment.
Where to Get Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids can be available from both animal and plant based sources. Here are some common food that contain omega-3s:
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish are excellent sources of EPA & DHA. Few examples like salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout, and tuna. Aim to include fatty fish in your diet at least twice a week to ensure an adequate intake of omega-3s.
- Fish Oil Supplements: If you don’t consume enough fatty fish, you can consider fish oil supplements. These supplements are available over the counter and deliver concentrated doses of EPA and DHA. It is recommended to discuss with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements.
- Algae: Algae-based supplements or foods derived from algae are a obtained of DHA, especially beneficial for vegetarians and vegans who avoid fish products. Algae-based omega-3 supplements are becoming increasingly popular and are comes in various forms like capsules and oil.
- Flaxseeds and Flaxseed Oil: Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil are wealthy in ALA, the plant-based omega-3 unsaturated fat. Ground flaxseeds are more effortlessly consumed by the body than entire seeds. You can add flaxseeds or flaxseed oil to smoothies, yogurts, grains, or use them as a fixing in baking.
- Chia Seeds: Chia seeds are another plant-based wellspring of omega-3s, especially ALA. They can be sprinkled over plates of mixed greens, added to smoothies, or utilized as an egg substitute in certain recipes.
- Walnuts: Walnuts are a decent wellspring of ALA and provide a variety of other nutrients. Enjoy a handful of walnuts as a snack, or add them to salads, oatmeal, or heated products.
- Soybeans and Soy Products: Soybeans and soy products, like tofu and edamame, contain omega-3 fatty acids. Counting these plant-based sources in your diet routine can help expanding your omega-3 intake.
- Hemp Seeds and Hemp Seed Oil: Hemp seeds & hemp seed oil contain ALA, and can be added to smoothies, salads, or utilized as a drizzle over cooked dishes.
It’s crucial to remember that the body’s ability to convert ALA to EPA and DHA is limited, so including animal-based sources of omega-3s or thinking about supplementation may be advantageous, particularly for people with particular dietary limitations or greater omega-3 demands.
Should You Take Omega-3 Supplements?
The decision to take omega-3 supplements should be based on individual health conditions and consultation with a medical professional. Here are a some facts to consider while choosing whether to take omega-3 supplements:
- Dietary Intake: Evaluate your current diet and assess whether you are regularly consuming omega-3 rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, or algae-based sources. If your diet lacks these food sources, supplementation might be beneficial to ensure get enough omega-3 fatty acids.
- Health Conditions: Omega-3 supplements may be helpful for some health conditions. For instance, doctors might suggest taking omega-3 supplements for people with excessive triglyceride levels, heart disease, or inflammatory disorders. To find out if supplementation is suitable for your unique condition, it is crucial to discuss with your healthcare provider.
- Vegetarian or Vegan Diet: If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet and do not consume any animal-based sources of omega-3s, you might be consider algae-based omega-3 supplements, which provide DHA. Consult with a healthcare professional for advice on suitable supplements.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, are vital for fetal brain and eye development during pregnancy and youth. Pregnant and breastfeeding ladies might be encouraged to take omega-3 supplements to guarantee sufficient admission. Be that as it may, it’s basic to get healthcare advice prior to starting any supplements when pregnant or breast-feeding.
- Blood Thinning Medications: Omega-3 fatty acids have delicate blood-reducing properties. Before incorporating omega-3 supplements into your regimen, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider. If you are on blood-thinning medications or have a bleeding disorder to avoid any potential interactions or complications.
- Overall Health Goals: If you have specific health goals such as improving cardiovascular health, reducing inflammation, or supporting brain function. Omega-3 supplements may be beneficial. It’s crucial to remember that supplements should complement a healthy diet, not replace it entirely.
Keep in mind, it is always best to consult with a doctors who can evaluate your individual needs, assess any potential risks or interactions, and provide personalized recommendations on whether omega-3 supplementation is suitable for you or not. Also they can guide you appropriate dosage and duration of supplementation if it’s recommended.
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids are critical supplements that have a large group of health benefits. They assume significant parts in heart health, brain capability, inflammation decrease, joint health, eye health, and temperament guideline. Both animal-based sources (fatty fish) and plant-based sources (flaxseeds, chia seeds, pecans) provide omega-3 fatty acids.
However, the body’s conversion of plant-based omega-3s (ALA) to the more beneficial EPA and DHA forms is limited. If dietary intake is insufficient, consider omega-3 supplements like fish oil or algae-based options. It’s vital to talk with a healthcare professional to decide whether supplementation is necessary and suitable for your particular conditions. Considering individual needs and health issues, a balanced diet is vital for optimizing overall health and well-being.