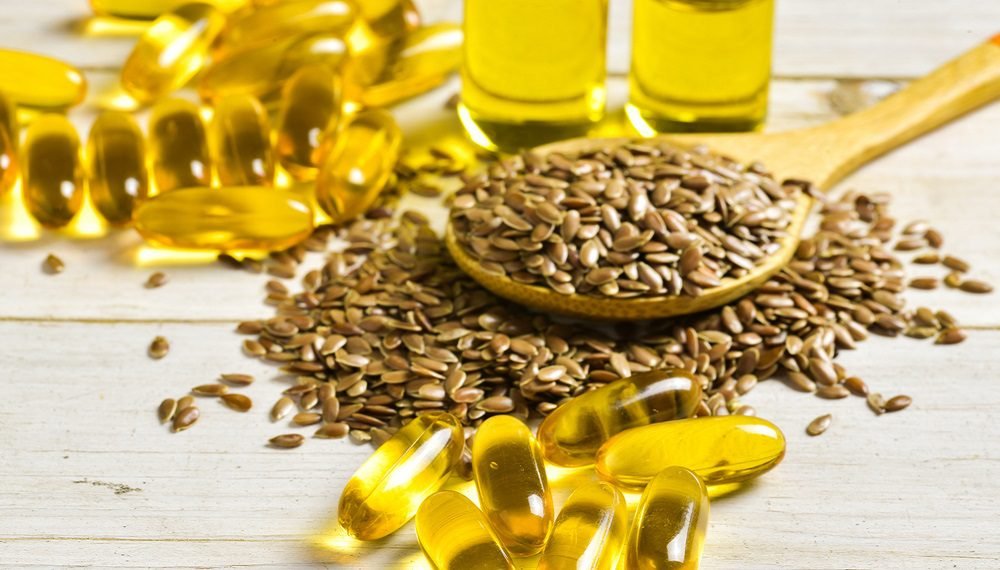
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is a fundamental omega-3 fatty acid. It is classified as an essential fatty acid because the human body cannot produce it and must obtain it from the diet.
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is a crucial omega-3 fatty acid present in plant-based sources. While it offers some medical advantages, including cardiovascular health and anti-inflammatory impacts, it is essential to acquire EPA and DHA straightforwardly from dietary hotspots for ideal medical advantages.
Talking with a medical services proficient or an enlisted dietitian can give customized exhortation on integrating ALA and omega-3 fatty acid into your diet in view of your particular requirements and health considerations.
Essential Fatty Acid: ALA is classified as an essential fatty acid because the human body cannot synthesize it and must obtain it through the diet. It is one of the three principal sorts of omega-3 fatty acids, close by eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Structure and Sources: ALA is a polyunsaturated fatty acid with 18 carbon molecules and three double bonds. It is fundamentally found in plant-based sources. Normal dietary sources of ALA incorporate flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, pecans, soybeans, and their oils. Certain green verdant vegetables and vegetable oils like canola oil additionally contain ALA, albeit in more modest amounts.
Health Benefits: ALA itself offers some health advantages, fundamentally connected with its role as an omega-3 fatty acid. It is linked to cardiovascular health, reduces the risk of heart disease, improves lipid profile, and lowers blood pressure. ALA additionally shows calming properties and may emphatically affect cerebrum health and mental capability. Note that the benefits of EPA and DHA may not directly apply to ALA due to limited conversion. These benefits include:
- Heart Health: ALA has been related with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease. It helps lower triglyceride levels, reduce inflammation, improve blood vessel function, and maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
- Brain Function: Omega-3 fatty acids, including ALA, are fundamental for appropriate brain capability and advancement. They support mental capability, memory, and learning. A sufficient dose of ALA has linked to reducing the risk of mental degradation and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Inflammation Reduction: ALA has anti-inflammatory properties. It decreases irritation in the body by tweaking the creation of inflammatory molecules. This calming impact might be helpful in overseeing persistent chronic inflammatory like rheumatoid joint pain, provocative gut sickness, and asthma.
- Skin Health: Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) keeps up with solid skin by supporting the construction and capability of cell layers, advancing moisture maintenance, and reducing inflammation. It might add to further developed skin appearance and reduce the risk of skin problems like eczema and psoriasis.
Conversion to EPA and DHA: Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) fills in as a forerunner for the creation of EPA and DHA in the body. However, the conversion process is limited and inefficient. The body converts only a small portion of ALA to EPA and DHA. Therefore, experts recommend obtaining them directly from dietary sources.
Recommended Dosage: The sufficient dosage of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) fluctuates relying upon age, gender, and specific health conditions. For adults, around 1.6 grams (1600 mg) each day for men and 1.1 grams (1100 mg) each day for ladies. It’s critical to get alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) through a reasonable eating routine that incorporates an assortment of plant-based sources.
Balancing Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Keeping a legitimate harmony between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the diet is significant. Many common vegetable oils, such as soybean oil, corn oil, and sunflower oil, contain omega-6 fatty acids. An irregularity, with unnecessary omega-6 and deficient omega-3 dosage, may add to inflammation and other medical problems. Eating various whole foods and limiting processed foods high in omega-6 oils maintains a healthy omega-3 to omega-6 ratio.
Conclusion
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) benefits health, but the body’s conversion to EPA and DHA is limited. Therefore, if you do not obtain sufficient amounts of EPA and DHA from foods, consider directly incorporating them into your diet or supplementing. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can offer personalized advice on incorporating ALA and omega-3 fatty acids into your diet.